Modern digital experiences depend on an invisible network that connects our world. This network links devices to share information, resources, and services easily.
From streaming movies to global business, these systems are the networking backbone of today. They allow instant communication worldwide and power cloud services that drive new ideas.
Learning what is a computer network shows how much they impact our daily lives. These systems are the key structure of our connected world.
As we dive into this digital communication foundation, we see the basic structure of modern tech. This web of connections truly defines our digital era.
Understanding the Core Definition
Computer networks are key to our digital world. They let devices talk and share info over long distances. This has changed how we communicate and share information.
What Constitutes a Computer Network
A network starts when two or more devices connect to share resources. These connected systems are called nodes or hosts. They form the base of any network.
Devices talk to each other using rules called communication protocols. These rules help data move smoothly between devices, no matter where they are or who made them.
Key Components and Their Functions
Every network needs specific hardware and logical parts to work well. Knowing these parts helps us understand how networks keep connections strong.
Nodes are any device on the network, like computers or phones. Each node has its own address to help it talk to others.
Routers are smart devices that send data between networks. They look at where data is going and find the best path.
Switches connect devices in one network. They make sure data gets to where it needs to go, making the network faster.
Servers offer resources and services to other devices. They host apps, store files, and manage the network, acting as hubs.
Communication protocols set the rules for how devices talk to each other. Standards like TCP/IP help different devices understand each other, even if they’re different.
| Component | Primary Function | Network Scope | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes | Endpoint communication | Local or remote | Unique addressing, resource sharing |
| Routers | Inter-network directing | Between networks | Path determination, traffic management |
| Switches | Intra-network connecting | Within single network | Port management, efficiency optimisation |
| Servers | Resource providing | Network-wide | Centralised services, high capacity |
| Protocols | Communication governing | Throughout network | Standardised rules, interoperability enabling |
These parts work together to make networks that support our digital lives. They help us share and communicate smoothly every day.
The Evolution of Networking Technologies
The journey of computer networking is truly remarkable. It has changed how we communicate, work, and access information. From isolated systems to a global network, it’s a huge leap forward.

From ARPANET to Modern Infrastructure
In the 1960s, the US Department of Defence started ARPANET. It was the first network to use packet switching. This connected four universities in 1969, starting the first wide-area network.
Paul Baran and Donald Davies came up with packet switching. This lets data travel in packets, reassembling at the end. It was much better than old methods.
ARPANET led to the internet. In the 1970s and 1980s, networking grew for both government and business. The 1983 introduction of TCP/IP made networks talk to each other, creating the internet we use today.
Now, we have cloud and software-defined networks. These support AI, IoT, and fast global communication. It’s far beyond ARPANET’s early days.
Milestones in Network Development
The history of networking has key moments. In 1940, George Stibitz showed remote computer access. It was an early network example.
The 1950s saw big steps with SAGE, a military network. It connected computers across sites, showing early distributed computing.
Important evolution of internet tech includes:
- 1969: First ARPANET connections
- 1971: First email sent across networks
- 1983: TCP/IP becomes standard protocol
- 1991: World Wide Web goes public
These milestones changed networking from a niche to a global tool. Each step built on the last, making today’s network possible.
Types of Computer Networks
Networks vary based on their range and how they connect. This creates different types for various uses. Knowing these helps pick the right one for your needs.
Local Area Networks (LANs)
LANs are common in daily life. They link devices in a small area, like a building or campus.
Characteristics and Common Uses
LANs are fast and reliable. They’re great for sharing resources. You can use Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi.
They’re used for sharing files, accessing printers, and using software together. Schools and offices use LANs a lot.
LANs are easy to manage and secure. Even homes with many devices act like LANs.
Wide Area Networks (WANs)
WANs connect far-off places. They link LANs across cities, countries, or continents.
Global Connectivity Solutions
WANs use technologies like leased lines and fibre optic cables. They’re key for global communication.
Big companies use WANs to link offices. The internet is the biggest WAN.
WANs support global business and cloud services. They focus on reliability over speed.
Wireless Networks
Wireless networks use radio waves instead of cables. They’ve changed how we connect devices.
Wi-Fi and Mobile Technologies
Wi-Fi gives wireless access in homes, offices, and public places. It follows IEEE 802.11 standards.
Mobile networks like 4G and 5G offer wide wireless coverage. They let you access the internet almost anywhere.
Wireless LANs mix LANs with wireless ease. Today, many use both wired and wireless networks.
| Network Type | Coverage Range | Typical Speed | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| LAN | Building/Campus | 1 Gbps – 10 Gbps | Office networks, home networks |
| WAN | Cities/Countries | 10 Mbps – 100 Mbps | Corporate networks, internet backbone |
| WLAN | Building/Campus | 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps | Mobile office access, public hotspots |
| Mobile Networks | Regional/National | 10 Mbps – 100 Mbps | Smartphone connectivity, IoT devices |
Each network type has its own role in today’s digital world. The right choice depends on your needs for coverage, speed, and mobility.
Network Topologies and Architectures
Network design is about how devices are connected and how they share resources. Topology and architecture are key. They affect a network’s performance and reliability.
Common Network Layouts
A network topology shows how devices are set up in a network. Different layouts have their pros and cons. This makes some topologies better for certain tasks.
The star topology has all devices connected to a central point. It makes troubleshooting easier and allows for adding new devices. If one connection breaks, it doesn’t stop the whole network.
In a ring topology, data moves in one direction around a circle. Each device is connected to two others. This design stops data collisions but can fail if a device breaks.
Bus topology uses one cable for all devices. It’s simple and cheap for small networks. But, the whole network can fail if the main cable has problems.
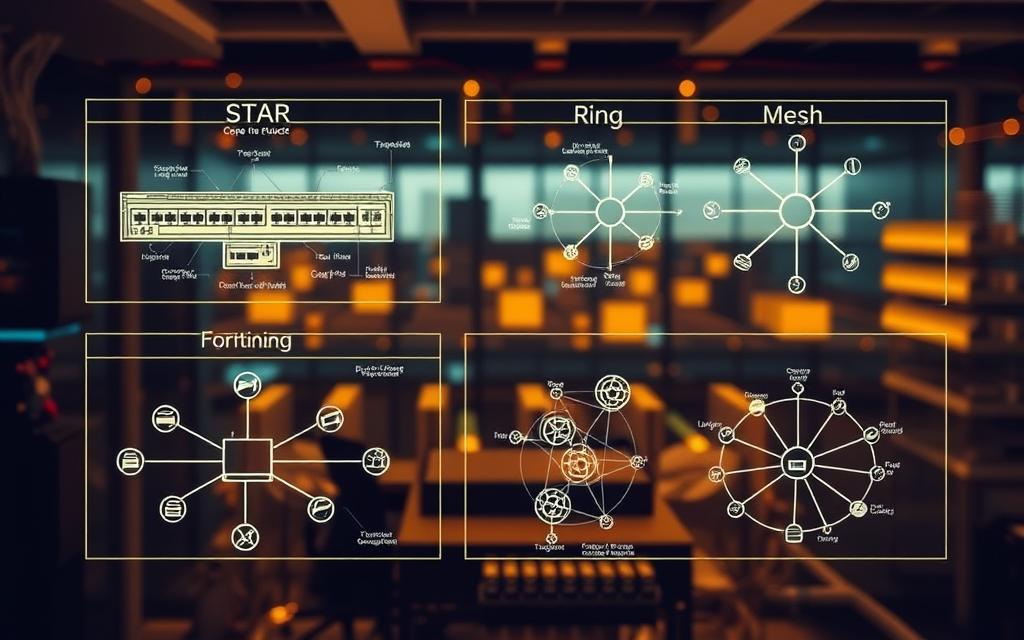
Mesh topology has many paths between devices. A full mesh has every device connected to every other. A partial mesh has some redundant paths. This design is reliable but complex and expensive.
Client-Server vs Peer-to-Peer Models
Network architecture is about how resources are shared. There are two main models: client-server and peer-to-peer.
The client-server model has servers managing resources. Clients ask for services from these servers. This model offers:
- Enhanced security controls
- Simplified data backup procedures
- Easier resource management
- Better performance for large networks
Businesses often choose client-server for its reliability and security.
The P2P (peer-to-peer) model treats all devices as equals. Each device can share resources directly with others. This model is good for small networks and home use because it’s:
- Lower in cost
- Easier to set up
- Doesn’t need dedicated servers
- Flexible in resource sharing
P2P networks are great for small offices and homes where users share files directly.
| Feature | Client-Server Architecture | Peer-to-Peer Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Centralisation | Centralised resources | Decentralised resources |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower implementation cost |
| Security | Enhanced security controls | Basic security features |
| Scalability | Excellent for large networks | Best for small networks |
| Management | Centralised administration | Distributed management |
Choosing the right network architecture depends on your needs. Think about network size, security, and budget when deciding.
Protocols and Standards Governing Networks
Networks work together thanks to communication protocols and technical standards. These rules help devices talk to each other, sending data where it needs to go. Without them, our digital world wouldn’t be the same.
The Role of TCP/IP
The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol suite is key for the internet. It has four layers, each focusing on different parts of sending data. The Network Access Layer deals with physical connections and addresses.
The Internet Layer handles logical addresses and routes data between networks. The Transport Layer makes sure data is delivered right, checking for errors and controlling flow. The Application Layer offers services to user apps. This structure helps in development and troubleshooting, keeping global networks strong.
“Many modern networks run on TCP/IP models, which include four network layers that work together to prepare, address, route, and deliver data efficiently across diverse network environments.”
Importance of IEEE Standards
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers is vital in setting technical standards. The IEEE 802 family of standards focuses on local and metropolitan area networks. This ensures consistency among different manufacturers and technologies.
Ethernet uses IEEE 802.3 for wired networks. Wireless networks, or Wi-Fi, follow IEEE 802.11. These standards let devices from various makers work together, encouraging innovation.
IEEE standards keep networking protocols compatible with the past while supporting new technologies. This mix of stability and progress makes today’s networks reliable and ready for the future.
Network Hardware Essentials
Every network has special hardware and media for data exchange. These parts are key for digital communication. Choosing and using them well is vital for network success.

Routers, Switches, and Hubs
It’s important to know what each network device does. A router directs traffic between networks. It checks data packets and picks the best path. Modern routers also have firewalls and can change network addresses.
A network switch works within one network. It makes special paths for data between devices. This makes networks more efficient and secure.
Hubs are older tech that sends data to all devices. They’re not used much now. But knowing about hubs shows how network tech has improved.
Cabling and Connectivity Options
There are many ways to connect devices for data transfer. Ethernet cable, like Cat5e and Cat6, is common for local networks. It’s reliable and affordable.
Fibre optic cabling is better for fast data over long distances. It uses light pulses in glass or plastic fibres. This means faster speeds and less interference.
Wireless tech has changed how we connect. It uses radio waves (Wi-Fi) and light. Each has its own benefits:
- Copper cables: Cost-effective and easy to install
- Fibre optics: High bandwidth and long-distance capability
- Wireless: Mobility and installation flexibility
Choosing the right network hardware is about performance, cost, and future needs. Getting a pro to install it can make networks more reliable for businesses.
Security Considerations in Modern Networking
Digital networks are now key to business and daily life. Protecting these systems against new threats is essential. Modern network security needs a layered approach, covering technical and human aspects.

Common Threats and Vulnerabilities
Today’s networks face many threats that can harm data and operations. Malware, like viruses and ransomware, is a big risk. It can spread fast across devices.
DDoS attacks flood networks with traffic, making services unavailable. These attacks use botnets to increase their effect.
Hacking and social engineering attacks, like phishing, keep evolving. They aim to exploit human psychology, not just technical weaknesses.
Many breaches come from unpatched software, misconfigured systems, or weak passwords. Staying alert to these threats is vital for organisations.
Best Practices for Network Protection
Strong network protection needs tech solutions and policies. A good security plan covers many defence layers.
Firewalls are the first defence, controlling network traffic. Next-generation firewalls offer advanced features like deep packet inspection.
VPNs create secure tunnels for remote access. They protect data in transit, essential for remote work.
Strong authentication, like MFA, greatly improves security. It requires two or more verification steps, reducing access risks.
Keeping software up to date is critical. Organisations should have formal patch management procedures.
| Security Measure | Primary Function | Implementation Level | Effectiveness Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firewall | Network traffic filtering | Network perimeter | High |
| VPN | Secure remote access | Connection level | High |
| MFA | User authentication | Application level | Very High |
| Regular Updates | Vulnerability patching | System level | Critical |
| Intrusion Detection | Threat monitoring | Network-wide | Medium-High |
Other measures include intrusion detection, proxy servers, and single sign-on solutions. Having a good incident response plan is also key.
Training employees is vital, as human mistakes can lead to security issues. Regular security awareness helps staff avoid threats, completing the protection circle.
Conclusion
Computer networks are key to our digital world. They connect everything from big companies to our homes. This lets us talk, work together, and shop online like never before.
But with these benefits comes the need for strong security. As networks get more complex, keeping them safe is more important than ever. This is true for all kinds of networks, not just the big ones.
The future of networking looks bright. We’ll see more use of artificial intelligence and better cloud systems. Companies like Cisco and Juniper Networks will keep making our digital lives easier. Networks will keep being the backbone of our connected world.
FAQ
What is a computer network?
A computer network connects devices to share data and resources. These devices, or nodes, use rules called protocols to communicate. Networks are key to modern digital life, supporting everything from emails to global business.
What are the main components of a computer network?
Key parts include nodes, routers, switches, and protocols. Cabling and wireless media, along with hardware, are also vital. They help build and keep networks running smoothly.
How did computer networks evolve historically?
Networking started with isolated mainframes, evolving to connected systems. ARPANET, funded by the U.S. Department of Defence in the late 1960s, was a key start. Standards developed later enabled today’s internet and cloud systems.
What are the different types of computer networks?
Networks vary by size and connection type. LANs cover small areas, while WANs span larger regions. Wireless networks, like Wi-Fi, offer cable-free connectivity.
What is meant by network topology?
Topology shows how devices are arranged in a network. Common layouts include star, ring, bus, and mesh. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks.
What is the difference between client-server and peer-to-peer architectures?
Client-server models have centralised servers for resources. Peer-to-peer (P2P) models share resources directly between devices. P2P is used for file-sharing and decentralised networks.
Why are protocols like TCP/IP important in networking?
Protocols like TCP/IP ensure devices from different makers can work together. They structure data handling across four layers, making internet communication possible.
What role do IEEE standards play in networking?
IEEE standards ensure network hardware and software work together. They include Ethernet and Wi-Fi standards, making device interoperability possible.
What hardware is essential for building a network?
Key hardware includes routers, switches, and cabling. Wireless access points and network adapters are also essential for Wi-Fi connectivity.
What are common security threats to computer networks?
Networks face threats like malware, DDoS attacks, and hacking. These risks highlight the need for strong security measures.
How can networks be protected against security risks?
Protect networks with firewalls, VPNs, and MFA. Keep software updated and conduct regular security audits. Educating users is also key.
What is the significance of wireless networks like Wi-Fi and 5G?
Wireless networks offer flexibility and mobility. They support a wide range of applications, from IoT to mobile internet, driving innovation.
How do fibre-optic cables compare to traditional copper cabling?
Fibre-optic cables have higher bandwidth and faster speeds than copper cables. They are more expensive but offer better performance and reliability.















